Circular economy is a central pillar of the EU Green Deal, which sets the new agenda for sustainable growth. In a circular economy, the value of the products, materials and resources is kept as long as possible, the production of waste is minimised and innovation is at the centre of the entire value chain. These concepts lie at the foundation of the European PVC value chain, embodied in the VinylPlus® Commitment to sustainable development.
PVC CABLE RECYCLING
PVC cables are easy to recycle mechanically and have a high recycling track record rate in Europe. Cables recycling typically follow two different streams:

1. WEEE AND ELV
Cables subject to one or both relevant European directives: WEEE (Waste from Electrical and Electronic Equipment) or ELV (End of Life Vehicles). In these cases, there is a general obligation to recover and recycle end-of-life electrical and electronic equipment and vehicles sent to demolition, although without a direct, explicit obligation for cables.
2. VINYLPLUS
Cables not subject to the WEEE and ELV directives, such as electric cables for power transmission and data transmission cables. This kind of end-of-life PVC cables is recycled within VinylPlus, the European PVC industry’s Commitment to sustainable development. Thanks to VinylPlus’ collection and recycling schemes, almost 1.7 million tonnes of PVC from cables were recycled since 2000. This is equivalent to almost 3.4 million tonnes of CO₂ emissions.
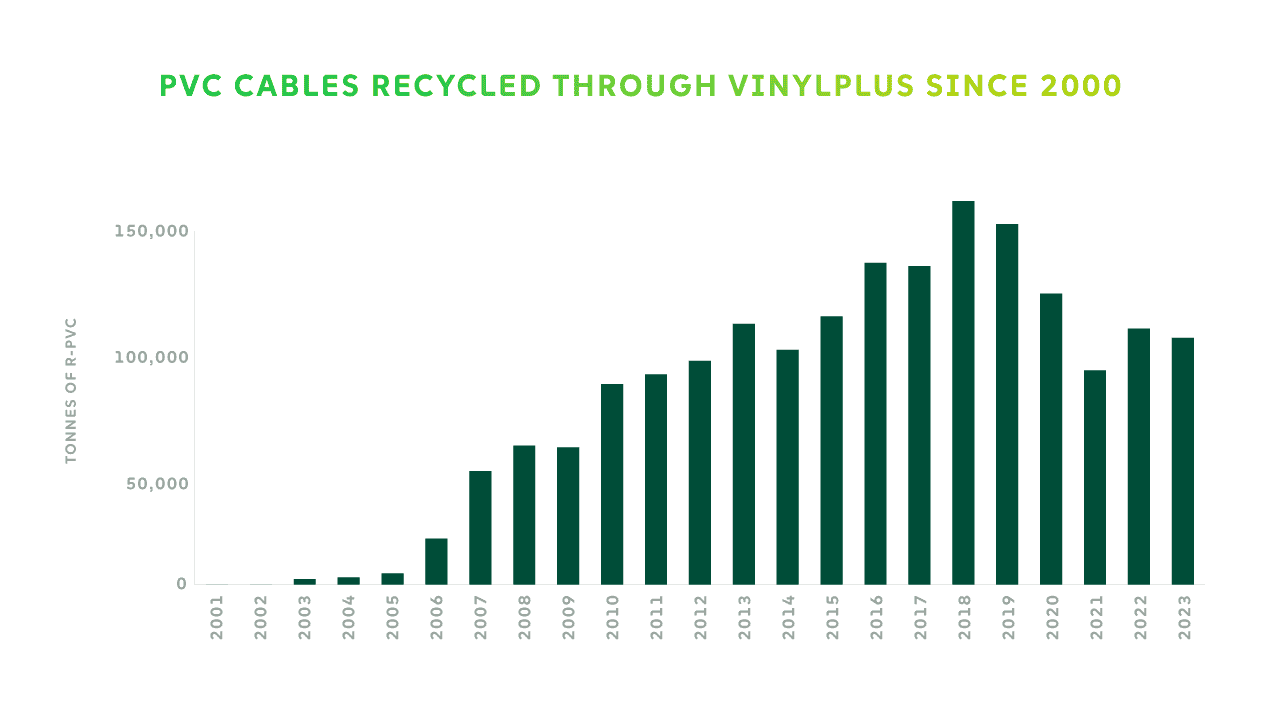
PVC cable recycling registered a significant decrease in recent years. This is mainly due to regulatory uncertainties and constraints at the EU level in relation to the potential presence of legacy additives in old PVC cables, even though new PVC cables produced in Europe today do not contain substances of very high concern (SVHC). But also, as for other PVC applications and plastics in general, to the persistent competitive prices of virgin material as well as to the slowdown of the building and construction sector.
THE PVC CABLE RECYCLING PROCESS



DID YOU KNOW?
PVC recycled from cables replaces virgin plastic on the market. Recycled PVC’s primary energy demand is up to 90% lower than virgin PVC, and by using recyclates valuable raw materials are conserved.
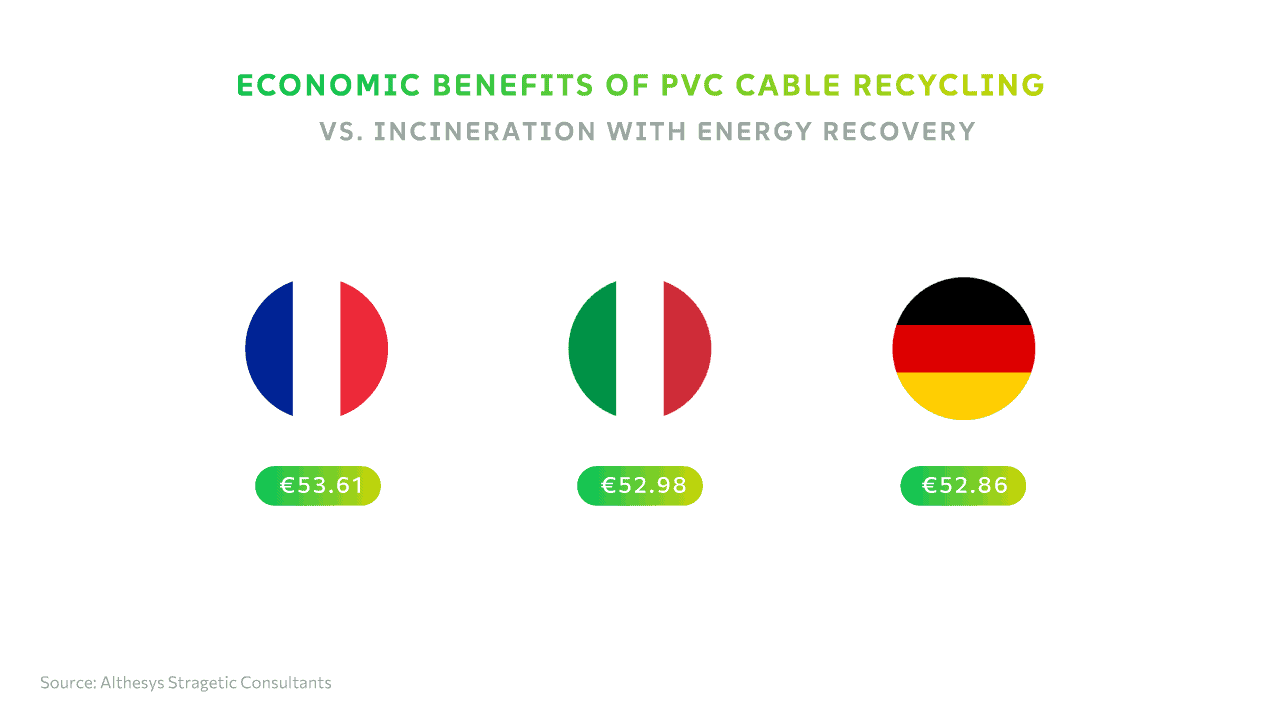
CABLE RECYCLING IS PROFITABLE
There are clear economic benefits from recycling of PVC cables. According to a recent study by Althesys Strategic Consultants, the economic benefits of recycling instead of incineration with copper recovery is around €53 pr. 100 metre cable.
EMBRACING THE CIRCULAR ECONOMY: ACHIEVING MORE WITH LESS
The circular economy embodies the philosophy of 'achieving more with less'—generating greater value with minimal environmental impact and optimized economic efficiency. This paradigm, as articulated by the European Commission, can manifest in a variety of ways, such as:
- Diminishing the volume of materials necessary to provide a specific service, often referred to as 'light-weighting'.
- Extending the lifespan of products to increase their utility and durability.
- Enhancing production and usage efficiency to decrease energy and material consumption.
- Minimising the use of substances or processes that obstruct recycling, an approach known as 'substitution'.
VINYLPLUS: PIONEERING A CIRCULAR FUTURE FOR THE EUROPEAN PVC INDUSTRY
Through its comprehensive VinylPlus Commitment to sustainable development, the European PVC industry is ideally situated to transition progressively towards a genuine circular economy model.
PVC is inherently a low carbon plastic, with 57% of its molecular weight stemming from chlorine derived from common salt, leading to reduced primary energy consumption during the manufacturing phase. Moreover, thanks to innovative breakthroughs and targeted investments, the market has seen the introduction of bio-attributed and bio-circular PVC resin, as well as non-fossil based additives, marking a significant step forward in sustainable practices.
Under the umbrella of VinylPlus, the European PVC industry is committed to progressively reducing emissions of greenhouse gasses and other substances across the entire production chain.
This holistic approach involves determining and monitoring the carbon footprint of all components and production processes, setting stringent emission reduction targets, increasing the use of renewable energy, and harnessing technologies to maximise material efficiency. Further, significant investments have been made towards improving the collection and recycling of PVC cables and other products.
Through these concerted efforts, the industry strives to lessen its environmental impact while enhancing productivity.

