Cables are essential for modern society as they play a critical role in communication, power transmission, transportation, and various industrial applications. Without cables, many of our modern conveniences and systems would not be possible. PVC cables are found in all sectors where transmission of electricity or data is needed. PVC cables have a vital role to play in shaping our digital future.
WHERE IS PVC USED IN CABLES?
PVC, or polyvinyl chloride, is extensively used in the manufacturing of cables due to its versatility, electrical insulation properties, inherent flame-retardancy, and cost-effectiveness.
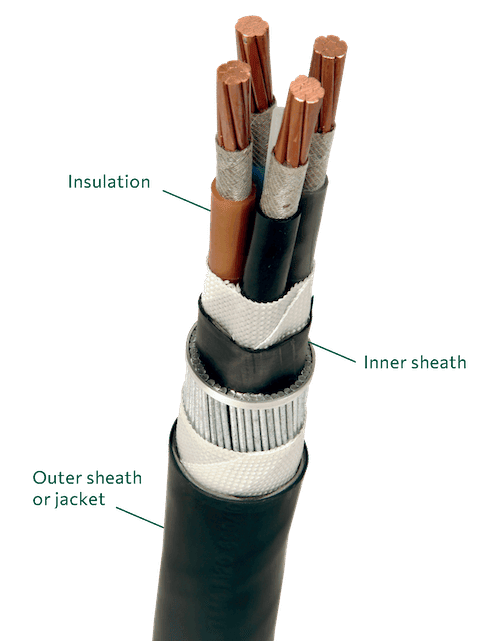
Insulation
One of the primary uses of PVC in cables is as an insulating material. This layer surrounds the conductor and prevents unintended current flow to other conductors or grounded surfaces.
Sheathing
Over the insulation, there's typically a sheathing layer, which can also be made of PVC. This layer provides additional protection to the cable, preventing mechanical damage, and also protects against environmental factors like moisture, chemicals, or UV radiation.
Outer Sheath
In multi-conductor cables, individual wires or pairs might be bundled together under an outer sheath or jacket, which can also be made from PVC. This outermost layer provides further mechanical protection and insulation.
ELECTRIC CABLES
PVC is widely used as classic electric cables for power transmission at low and medium voltage for homes, offices and industrial settings.
Contrary to common perception, electrical cables insulated with PVC are as fire-resistant as their halogen-free counterparts. PVC cables can obtain the highest fire reaction results compared with any other thermoplastic material, reaching B2Ca class, and d0 and S1a subclasses under the EU Construction Products Regulation (CPR).
PVC cables manufactured in Europe with compounds produced by VinylPlus and PVC4Cables partners do not contain DEHP phthalate or other substances of very high concern (SVHC), reflecting the value chain’s commitment to prioritising both safety and sustainability.
AUTOMOTIVE
PVC cables have many critical functions in cars, trucks, buses and other vehicles. PVC is used for the electrical wiring of headlights, taillights, and sensors. PVC battery cables connect the battery to the starter motor, alternator, and other electrical components. PVC ignition cables transmit the electrical energy from the ignition coil to the spark plugs.
PVC cables also bring comfort and joy for driver and passengers. Heating and air conditioning systems are often wired with PVC cables, as are speakers, amplifiers, and head units in audio systems.
The wide range of cable applications within the automotive sector is due to PVC’s excellent insulation properties, resistance to temperature changes, and ability to withstand exposure to oils, chemicals, and other harsh conditions.
INDUSTRY
PVC cables are widely used in electrical wiring and power distribution systems in manufacturing plants. They transmit power and signals from one point to another and are ideal for use in harsh industrial environments. PVC cables are also used in machinery wiring applications, where they connect machines and equipment, transmit signals, and control the operation of the machines.
Automation and robotics are needed to keep European manufacturing competitive, and here PVC cables have an important role to play. PVC cables are widely used in automation systems for industrial processes, where they to connect sensors, actuators and other control devices to the central control system. In robotics, PVC cables are used for data transfer, control, and power transmission.
TELECOMMUNICATIONS
The COVID-19 confinement period made it starkly apparent how crucial a stable internet connection is to our daily lives. As online meetings were intermittently disrupted by lagging connections, the importance of reliable physical infrastructure for digital connectivity became undeniable.
Polyvinyl Chloride, or PVC, plays a vital role in this context. It's commonly employed as an insulating material for telecommunication cables, safeguarding the conductors from potential damage caused by moisture, heat, and other environmental factors.
Telecommunication applications encompass a wide range of connectivity options. PVC is integral in the construction of telephone lines, ethernet cables, coaxial cables, and fiber optic cables, all of which are essential to our digital world.
In the absence of PVC-insulated cables, the ongoing digital transformation of Europe, and indeed the world, would be significantly hindered. This highlights the crucial role PVC plays in supporting the digital infrastructure that underpins our modern, connected society.
MEDICAL DEVICES
Innovations in healthcare technology is happening at rapid pace, with new diagnosis and treatment solutions being presented almost daily. In addition to traditional uses like patient monitoring devices, X-ray machines, and MRI scanners, PVC cables are increasingly being utilized in cutting-edge healthcare technology.
For instance, telemedicine solutions, which have seen a surge in usage due to the global shift towards remote healthcare, rely heavily on PVC cables for secure and reliable data transmission.
Advancements in surgical robotics also leverage PVC cables. These robots require cables that can handle repeated movements without degradation while providing a steady stream of power and data. Here too, PVC's flexibility and durability are key attributes.
CONSUMER ELECTRONICS
PVC cables are commonly used as power cords in consumer electronics, such as home appliance, computers, and televisions. They are flexible and durable, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
PVC audio cables for speakers, headphones, and microphones transmit high-quality audio signals and are also flexible, making them easy to maneuver.
PVC USB cables for smartphones, tablets, cameras and other consumer electronics transmit both power and data and are also durable, making them suitable for frequent use.
PVC ethernet cables for routers, switches, and modems ensure high-speed data connection. Importantly, PVC cables are flexible, making them easy to install.
WHERE ARE PVC CABLES FOUND IN YOUR HOME?
PVC cables are the backbone for powering a myriad of household and industrial appliances. From essential home devices like fridges, washing machines, and toasters to ubiquitous technologies such as TVs, PCs, laptops, smartphones, tablets, and other IT devices, PVC cables stand out as robust and dependable lifelines. These cables play a crucial role in connecting homes and offices, creating a sturdy network that facilitates seamless communication and power distribution globally.

OTHER PVC APPLICATIONS

CABLE DUCTS
A cable duct, sometimes referred to as a conduit or raceway, is a type of pathway or channel designed to hold and protect electrical wires or cables. PVC cable ducts provide a structured and safe route for cabling, helping to protect them from damage, which can be caused by impact, moisture, dust, or other environmental factors. They're commonly used in both residential and commercial buildings, as well as in industrial settings.
In larger installations, like data centres or telecommunications networks, cable ducts can also help manage large amounts of cabling in an organized way, making maintenance easier and more efficient.
PVC cable ducts, with their lightweight properties and ease of installation, significantly contribute to fostering a safe and efficient work environment.
CABLE TRAYS
Cable trays are like the 'highways' of the cable world - they allow for easy access, ventilation, and visual inspection of the cables. They are typically used in commercial and industrial settings where changes to the wiring system are expected to happen frequently.
PVC is favoured for cable trays due to its resistance to various chemicals, including acids, alkalis, and salts. Its durability enables it to withstand both indoor and outdoor environments, while its self-extinguishing nature provides added safety against fire incidents.In contrast to metal, PVC is a non-conductive material that offers excellent electrical insulation, hereby greatly minimising electrical shock hazards. In addition, PVC cable trays are lightweight, easy to handle, and very cost-effective due to their ease of installation.
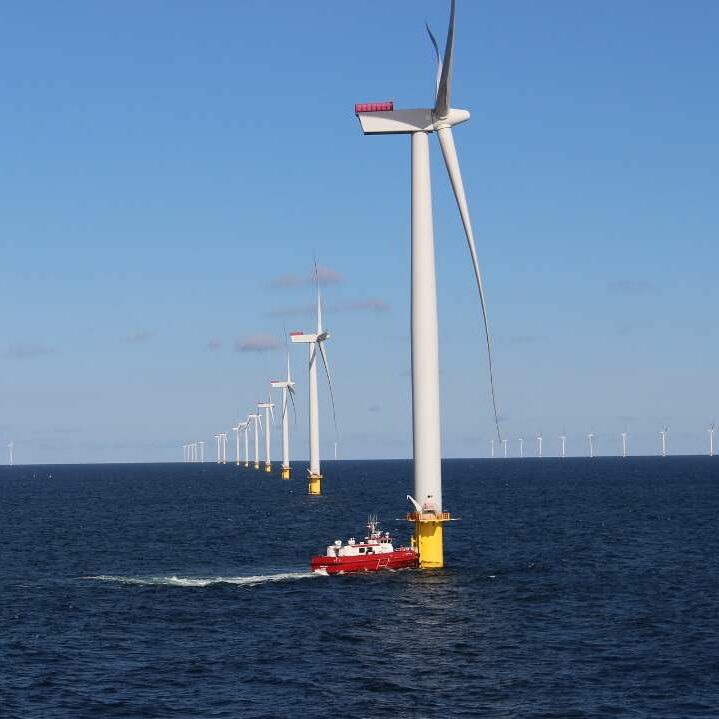

OFFSHORE AND SUBMARINE
Offshore and submarine environments present unique challenges for cable applications due to factors such as high pressures, extreme temperatures, corrosive seawater, and mechanical stresses associated with ocean waves and currents. Offshore wind farms, in particular, need robust and reliable transmission systems to transfer generated power to the onshore grid.
PVC is a popular choice for umbilicals, fiber enforced rods and shaped filler systems for power cables in these environments due to its excellent electrical insulation properties, flexibility, and resistance to environmental factors such as oxidation and weathering.


